- Connectors
Terminology - Connector Trivia vol.2 -


Here are some of the most common technical terms used in the connector industry, from terms related to the structure and parts of the connector to failure cases.
Connector Structure and Part Names
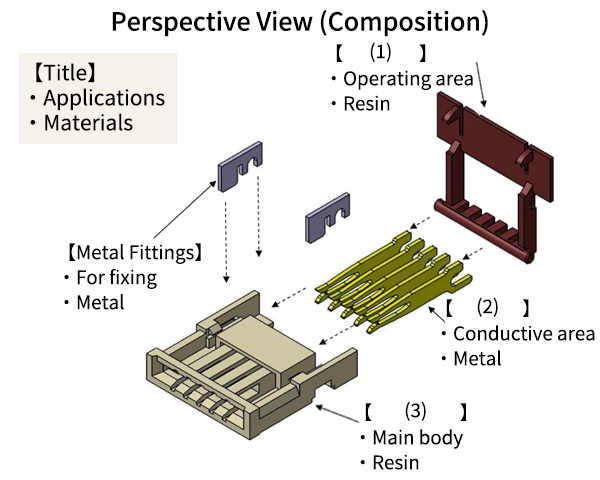
Here is a case of FPC connector to illustrate its composition.
A connector mainly consists of an actuator, metal fitting, contact, and insulator.
See below for each application and material. The meaning of each part is explained in the Glossary.
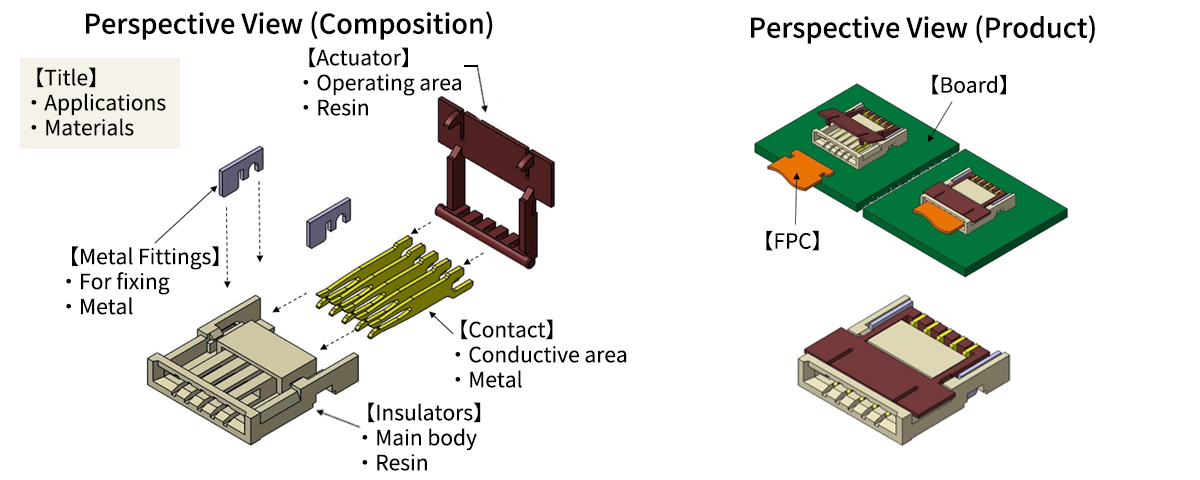
Glossary
Components and Related Terms
Components
| Name | Synonyms | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actuator | Slider | Parts to lock or temporary hold when mated. In case of FPC/FFC connector, parts that fix or hold the cable. |
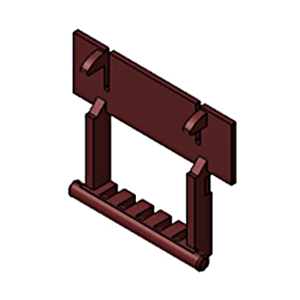 |
| Insulator | Molded part Resin part Housing |
Resin molded parts. The insulator that forms the entire connector and protects the contacts (wires). |
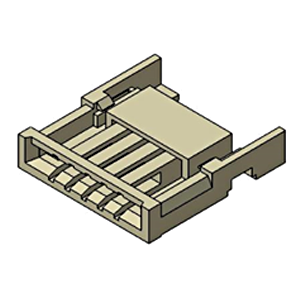 |
| Contact | Terminal | Metal parts to provide contact and energizing functions. | 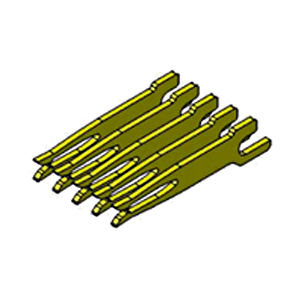 |
| Tail | Lead | Where the contacts/terminals are soldered. | |
Related Terms
| Name | Synonyms | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coplanarity | Flatness | Maximum height from board surface to contact tail. Variance of lead to board surface. |
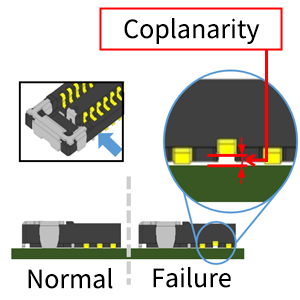 |
| Pitch | - | Distance between terminals. Set by miswiring prevention and rated current/voltage. |
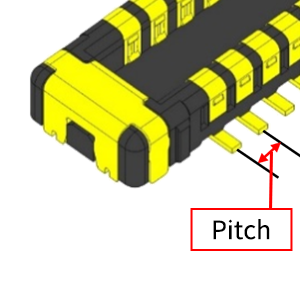 |
| Plug / Receptacle | Male / Female Headers / Sockets |
Plug: The part to insert the contact. The shape that is on the insertion side when it is mated. Receptacle: The part into which the contact is inserted. The shape that becomes the receiving side when mated. |
|
| FPC | Flex cable | Short for Flexible Printed Circuits. A cable with printed circuits. | 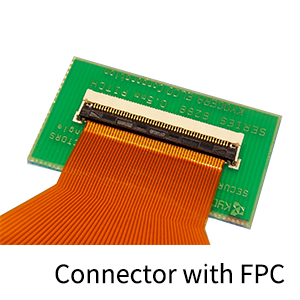 |
| FFC | Flex cable | Short for Flexible Flat Cable. A cable consisting of flat laminated wires. | 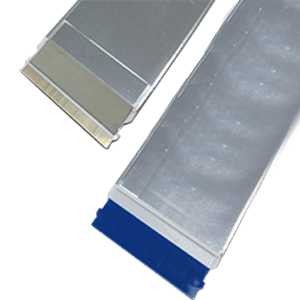 |
Type
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| ZIF | Short for Zero Insertion Force. When inserting or removing the FPC/FFC, the connector terminal and conductor of FPC/FFC are brought into contact and conducted by operating a locking mechanism such as an actuator/slider. A connector with reduced insertion and removal force.
|
 |
| Non-ZIF |
Connectors without ZIF structure. Insertion force is required when inserting the FPC/FFC into the connector. The connector terminal and conductor of the FPC/FFC are in constant contact from the moment they touch the terminal at the insertion port until they are pushed in. While the workability and cost are good, the cable retention force can be weak in case of small pin counts, and a high insertion force is required for high pin counts.
Related Terms
|
 |
| Vertical | The connector mating direction is perpendicular to the mounting board surface. | 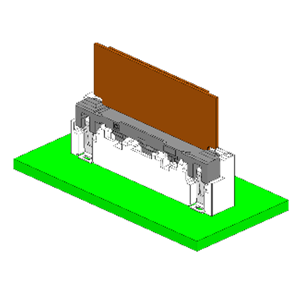 |
| Right Angle (RA) | The connector mating direction is horizontal to the mounting board surface. | 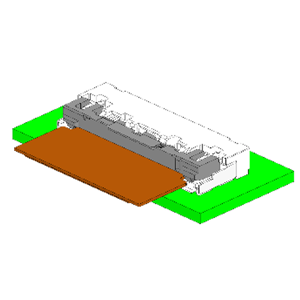 |
Terms for Failure Cases
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Weld | A line that forms a joint when molten materials, such as resin, solidify. |  |
| Crack | - | 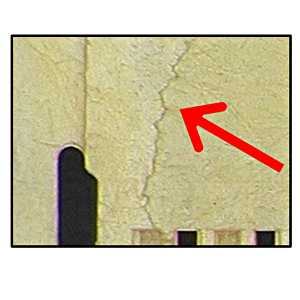 |
| Contamination | Foreign matter entering the resin. Dirty resin. | 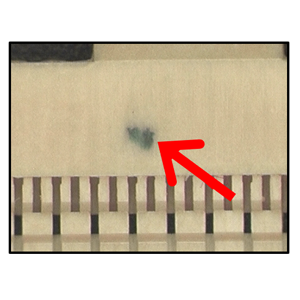 |
| Short shot | A lack of resin filling. | 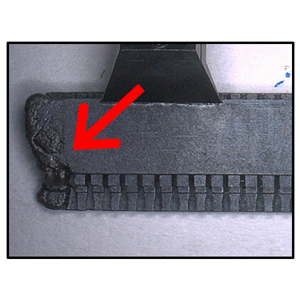 |
| Burrs | A protrusion that pops out of its normal shape. | 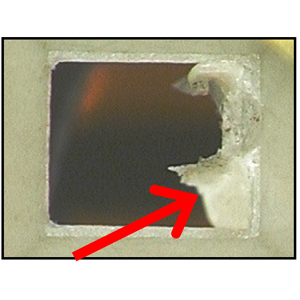 |
| Solder fillet | The shape when soldered. | 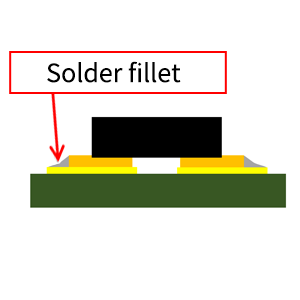 |
| Blisters | A blister-like phenomenon on the surface of the resin. Also called a bubble. |  |
Learn More About Connector Terminology Here Glossary of Electronic Components
Comprehension Test
Q. What is the name of (1) to (3)?
Tips
(1) Parts to lock or temporary hold when mated.
(2) Metal parts to provide contact and energizing functions.
(3) Resin molded parts.
Answer (Click to Check)
- A. (1)Actuator (2)Contact (3)Insulator
List of Connector Trivia Articles
vol.2 Terminology
vol.5 Evaluation Test (Basics)
vol.6 Evaluation Test (Special Edition)
vol.7 The History of Kyocera's FPC/FFC Connectors
vol.8 Evolution of FPC/FFC Connectors
vol.9 Basic Knowledge of Board to Board Connectors
vol.10 Learn more about Board to Board Connectors ~Various Features~
vol.11 Basic Knowledge of Plating








