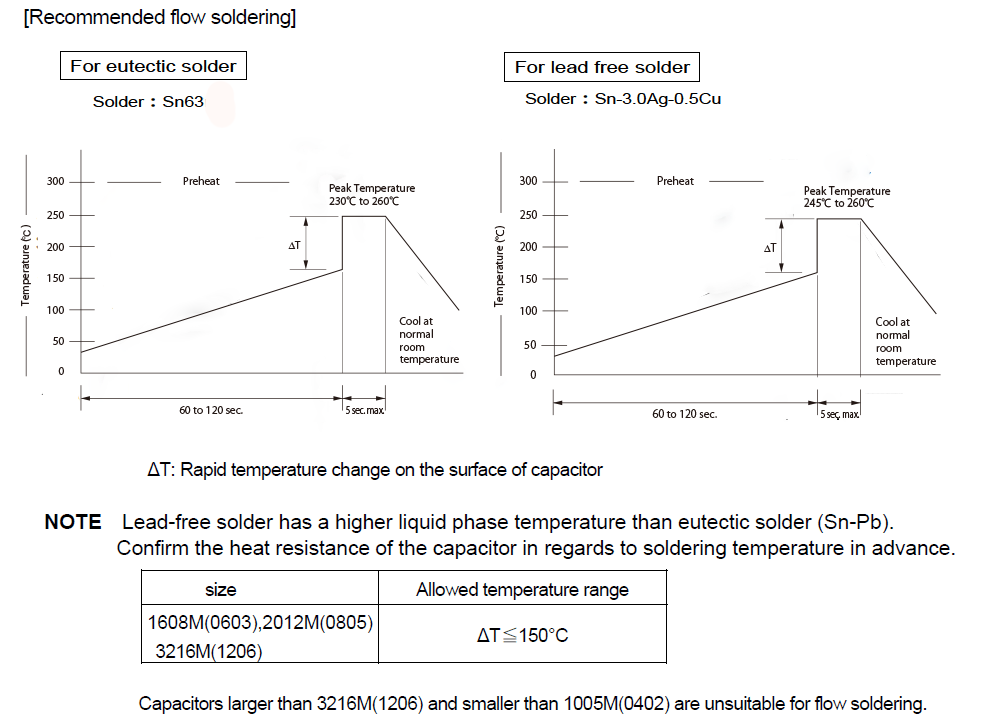
Flow soldering
The soldering conditions (preheating temperature, soldering temperature and their durations) shall be within the limits in the catalogs or product specifications. Perform soldering within these specifications.
When the capacitors are used exceeding the limits given in the catalogs or product specifications, cracks
may occur in the capacitors and the reliability may deteriorate, especially the rapid temperature changes
and partial heating during soldering may cause cracks. The temperature profile should be in accordance
with the catalogs or product specifications.
Generally recommended temperature conditions for flow soldering is as follows:
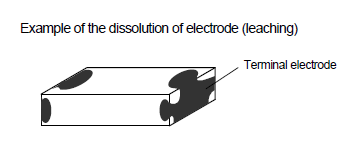
When the capacitors are soldered under long duration or high temperature, the dissolution of electrode (leaching), deterioration of adhesion (shear strength) and capacitance decrease may occur.
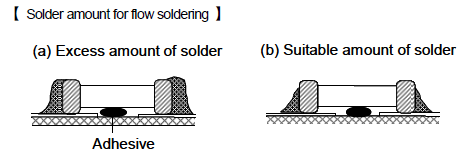
Proper amount of solder is required.
Excess solder generates high contraction stress. The capacitor may also be exposed to thermal and/or
mechanical stress resulting in cracks or breaks. Insufficient solder results in deficient capacitor
adherence to the printed wiring board, which may cause capacitor detachment or deficient electric
connection and reliability deterioration of the circuit may occurs.
Typical amount of solder are shown as follows.
Caution of flow soldering comparing to reflow soldering
Flow soldering shall not be applied to the capacitor designed for reflow soldering only.
Cracks due to thermal stress or dissolution of electrodes (leaching) may occur and may result in
deterioration of adhesion (shear strength) or decrease in capacitance.
Some large size and small size capacitors are unsuitable for flow soldering.Consult us for details.
Safety Application Guide for Multilayer Ceramic Chip Capacitors All Lists




