Glossary of Electronic Components
Connectors
[FPC/FFC connector] A latch with a locking mechanism that is actuated when connecting FPC/FFCs for retention.
Protrusions made by an embossing work. On connectors, a cylindrical protrusion(s) formed on an insulator housing for positioning the connector on a board. Also known as pegs.
Impedance is a value indicating resistance to AC currents, and it varies with frequency. Characteristic impedance is the impedance of a signal path, usually set to a certain value in equipment or a system.
A connecting device including accessories to join electrical circuits or equipment together.
Related Products Connectors
Terminals, leads or pins contained in connectors, or also contacting part of the terminal/lead/pin. Metal parts or metallic portions responsible for conducting electricity when connectors are mated or connected. There are various kinds of contacts, such as tuning forks and bellows.
The distance on the surface of a contact on which another contact touches and travels during mating/unmating; or contact margin.
Length of the surface of contacts that are touching one another during insertion or withdrawal. Means contact effective length.
Cracking of resin parts, cracking that extends to the inside due to external force and the like.
Dent on a portion of a contact, the protrusion formed on the other side of a dent accommodates the wiping effect. The holding strength by insulator housing is improved with the protruded part.
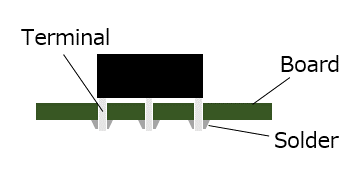
A method of mounting components on a printed circuit board (PCB) by inserting component leads to be soldered into through-holes of a PCB and dipping it into a solder bath to mount the components.
A carrier tape containing electronic components for surface mounting on PCBs. The tape itself is a packing material for SMT. The carrier tape with pockets holding the individual components that are sealed by a cover tape is called Embossed Tape Assembly or Tape & Reel Package.
Abbreviation of Electromagnetic Compatibility. The concept of enabling electronic devices to function without EMI.
Abbreviation of Electromagnetic Interference. A disturbance of an electrical circuit caused by external interference of an electromagnetic origin.
Abbreviation of Electromagnetic Susceptibility. The vulnerability of an electric circuit to a disturbance of electromagnetic origin.
Abbreviation of Flexible Flat Cable. Multiple thin rectangular conductors at regular intervals laminated with an insulating sheet.
Related Products FPC/FFC Connectors
It is an activator that improves solderability, and has oxide film removal and thermal conductivity effects.
Abbreviation of Flexible Printed Circuit. Circuit is printed on a thin insulating sheet with a conducting material.
Related Products FPC/FFC Connectors
An insulating body or generic name for insulating materials constituting the outer shell of a connector that holds or accommodates contacts or post pins. It is also called a housing or mold.
Solder tails are bent in order to firmly connect a board with a connector to prevent contacts from floating when soldered.
[FPC/FFC connector] Abbreviation of Low Insertion Force. A contact structure designed to suppress the mating force, while allowing enough force to retain a FFC/FPC.
To combine a connector to a compatible part for the purposes of transferring electricity.
[FPC/FFC connector] Property of connectors that do not have a ZIF structure. FPC/FFCs are inserted directly into this type of connector, relying on contact friction to retain the FPC/FFC.
Number of terminals/leads/circuits/contacts/ways contained in a connector.
Spacing between contacts. Center-line spacing of adjacent contacts.
A solderless method to mount components on a printed circuit board. Contacts are pressed into through holes of a printed circuit board to make a conductive connection. Because it is solderless, no solder bridges, contact failure due to flux splash or penetration, or thermal deterioration of material will occur.
Connector height from the board surface to the top face of the mounted connector.
A soldering method in which solder is applied to electronic components and then melted in a reflow oven to permanently mount them to a printed circuit board (PCB).
A horizontal connection type. Connectors oriented in a way where the mating portion of the contacts are parallel to the mounting surface.
Composed of an outer shell of a connector, to protect the insulator and secure the housing and aligns connectors to be mated. It has a structure to which necessary metal or the like can be attached. Also serves as a countermeasure against noise in high frequency (high-speed transmission) signals.
Abbreviation of Surface Mount Device. Components suitable for SMT equipment.
Abbreviation of Surface Mount Technology. A method of producing electronic circuits on a printed circuit board (PCB) by applying solder paste and placing components on the PCB's surface before the solder is melted in a reflow oven.
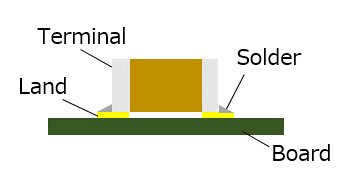
Distance between the two surfaces that the connectors are mounted on.
Distance space provided between connector bottom and board surface for securing mounting space or preventing flux-wicking.
A vertical connection type. Connectors oriented in a way that the mating portion of the contacts are perpendicular to the mounting surface.
Separating mated connectors or removing a mated object from a connector.
Growing hair-like crystals generated on the surface covered with tin-based plating or the like. Temperature, humidity, stress, and / or atmosphere prompt growth. The grown hair-like crystal would come into contact with adjacent parts (such as contacts), resulting in a short circuit.
The action in which a connector contact rubs the mating surface of another contact eliminating oxides/foreign substances adhering to the surface.
[FPC/FFC Connector] Abbreviation of Zero Insertion Force. When inserting or removing a FFC or the like to/from a ZIF connector, the actuator reduces insertion/removal forces by eliminating the need for friction of the contacts to retain the FFC or the like. All Non-ZIF type connectors do not have this structure.