전자부품 용어집
파워 디바이스
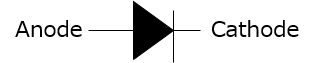
An electrode through which a current flows into a polarized electrical device.
[Diode] Maximum average forward current of commercial frequency (50Hz/60Hz) sin wave under condition.
[Thyristor] Maximum average on-state current of commercial frequency (50Hz/60Hz) half sin wave under specified condition.
An electrode from which a current leaves a polarized electrical device.

A two-terminal semiconductor device which conducts current in one direction, i.e. from anode to cathode, also called a rectifier.
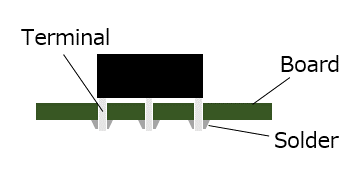
A method of mounting components on a printed circuit board (PCB) by inserting component leads to be soldered into through-holes of a PCB and dipping it into a solder bath to mount the components.
A semiconductor with a single function. For example, diodes and transistors.
Related Products Discretes General Rectifier Diodes Discretes Fast Recovery Diodes(FRD) Discretes Schottky Barrier Diodes(SBD) Discretes Avalanche Guaranteed Schottky Barrier Diodes
Abbreviation of Electromagnetic Interference. A disturbance of an electrical circuit caused by external interference of an electromagnetic origin.
Abbreviation of Electromagnetic Susceptibility. The vulnerability of an electric circuit to a disturbance of electromagnetic origin.
PN type junction rectifying device. Diodes suitable for rectifying high frequency power supply with short reverse recovery time (trr).
Related Products Discretes Fast Recovery Diodes(FRD) FRD/SBD Modules
Minimum gate current required to turn on.
Minimum gate voltage required to turn on.
PN type junction rectifying device. Diodes that rectifies a commercial frequency that is alternating current.
Related Products Discretes General Rectifier Diodes General Rectifier Diode Modules
Abbreviation of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor. A type of three-terminal power semiconductor device, with an insulated gate which controls the current flowing through the device. An IGBT features the voltage-driven characteristics of MOSFETs in addition to the high-current capability of bipolar transistors.
Range of junction temperature while operating.
Peak forward voltage at specified forward current.
Peak reverse current at specified reverse voltage
A soldering method in which solder is applied to electronic components and then melted in a reflow oven to permanently mount them to a printed circuit board (PCB).
Allowable peak off-state voltage repetitively applicable between anode and cathode.
[Diode]Allowable peak reverse voltage repetitively applicable to diode.
[Thyristor]Allowable peak reverse voltage repetitively applicable between anode and cathode.
[Diode]Allowable peak reverse voltage repetitively applicable to diode.
[Thyristor]Allowable peak reverse voltage repetitively applicable between anode and cathode.
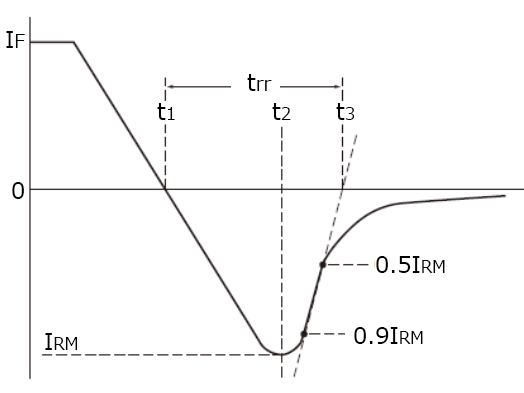
Diodes utilizing potential barrier (schottky barrier) formed at a junction between metal electrode and semiconductor.
Related Products Discretes Schottky Barrier Diodes(SBD) FRD/SBD Modules
Abbreviation of Surface Mount Device. Components suitable for SMT equipment.
Abbreviation of Surface Mount Technology. A method of producing electronic circuits on a printed circuit board (PCB) by applying solder paste and placing components on the PCB's surface before the solder is melted in a reflow oven.
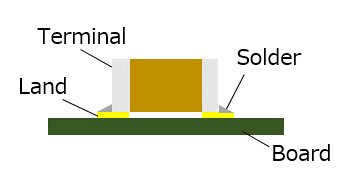
Range of ambient temperature while not operating.
Allowable peak reverse voltage non-repetitively applicable to diode.
Temperature difference per watt between two points, such as junction and ambient, or junction and case after thermal balance is established Rth(j-c): junction to case, Rth(j-l): junction to lead, Rth(j-a): junction to ambient.
A type of three-terminal power semiconductor device that conducts high current when the gate receives a current trigger.
Related Products Power Semiconductor device
A semiconductor device used to amplify or control current.